H7-Unit_4-Policy_Gradient_with_PyTorch-A0-Introduction
中英文对照学习,效果更佳!
原课程链接:https://huggingface.co/deep-rl-course/unit7/additional-readings?fw=pt
Introduction
引言

In the last unit, we learned about Deep Q-Learning. In this value-based deep reinforcement learning algorithm, we used a deep neural network to approximate the different Q-values for each possible action at a state.
在上一单元的缩略图中,我们了解了深度Q-Learning。在这种基于值的深度强化学习算法中,我们使用了深度神经网络来逼近一个状态下每个可能动作的不同Q值。
Since the beginning of the course, we only studied value-based methods, where we estimate a value function as an intermediate step towards finding an optimal policy.
自课程开始以来,我们只研究了基于价值的方法,在这种方法中,我们估计一个价值函数,作为寻找最优策略的中间步骤。
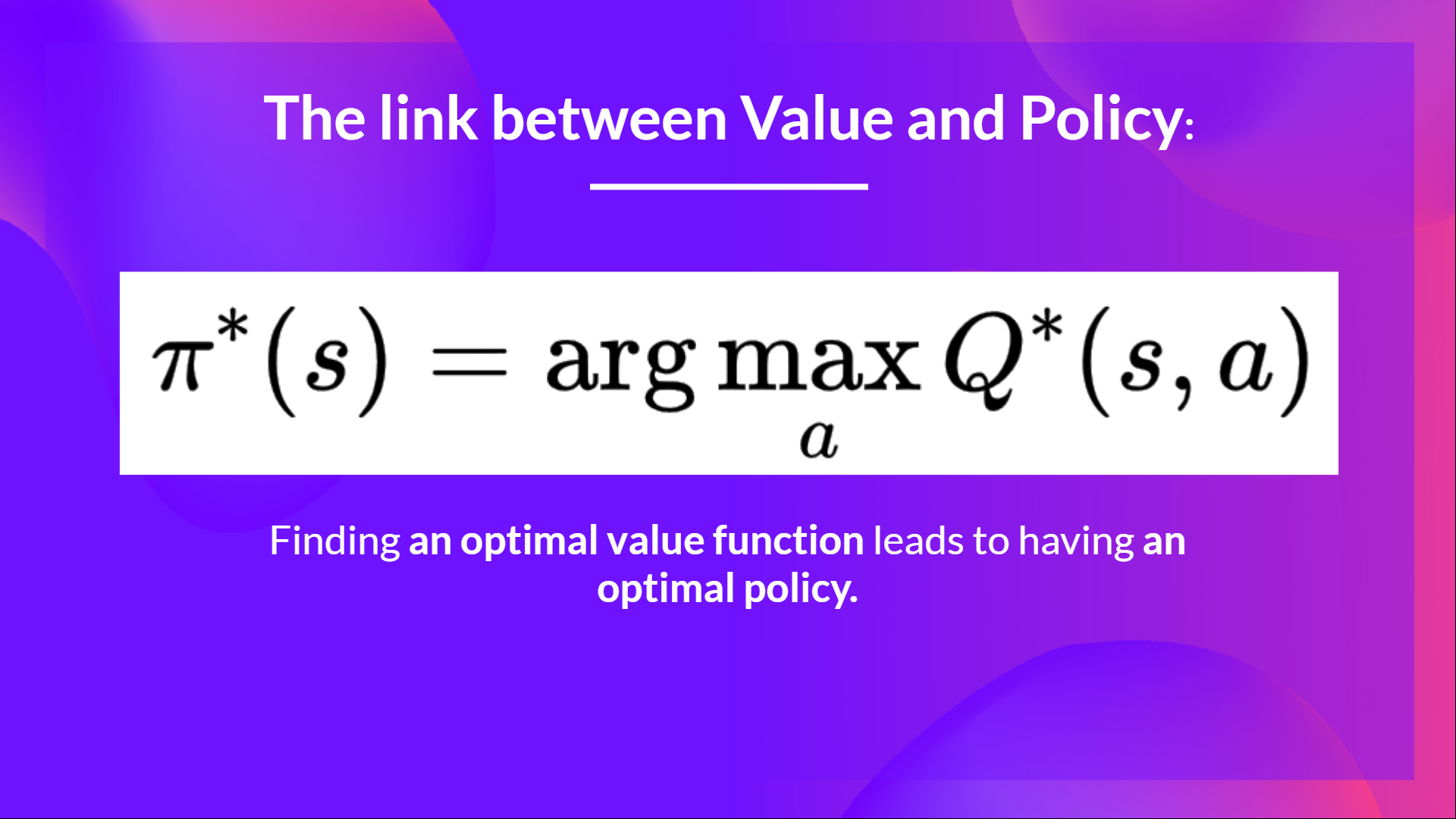
In value-based methods, the policy πππ only exists because of the action value estimates since the policy is just a function (for instance, greedy-policy) that will select the action with the highest value given a state.
链接值策略在基于值的方法中,策略πππ仅因为动作值估计而存在,因为策略只是一个函数(例如,贪婪策略),它将在给定的状态下选择具有最高值的动作。
But, with policy-based methods, we want to optimize the policy directly without having an intermediate step of learning a value function.
但是,使用基于政策的方法,我们希望直接优化政策,而不需要学习价值函数的中间步骤。
So today, we’ll learn about policy-based methods and study a subset of these methods called policy gradient. Then we’ll implement our first policy gradient algorithm called Monte Carlo Reinforce from scratch using PyTorch.
Then, we’ll test its robustness using the CartPole-v1 and PixelCopter environments.
所以今天,我们将学习基于政策的方法,并研究这些方法的一个子集,称为政策梯度。然后,我们将使用PyTorch从头开始实现我们的第一个策略梯度算法,称为蒙特卡洛强化。然后,我们将使用CartPole-v1和PixelCopter环境测试其健壮性。
You’ll then be able to iterate and improve this implementation for more advanced environments.
然后,您将能够在更高级的环境中迭代和改进此实现。
Let’s get started,
环境让我们开始吧,