E4-Unit_2-Introduction_to_Q_Learning-I8-A_Q_Learning_example
中英文对照学习,效果更佳!
原课程链接:https://huggingface.co/deep-rl-course/unit5/bonus?fw=pt
A Q-Learning example
一个问答学习的例子
To better understand Q-Learning, let’s take a simple example:
为了更好地理解Q-Learning,让我们举一个简单的例子:

迷宫–例子
- You’re a mouse in this tiny maze. You always start at the same starting point.
- The goal is to eat the big pile of cheese at the bottom right-hand corner and avoid the poison. After all, who doesn’t like cheese?
- The episode ends if we eat the poison, eat the big pile of cheese or if we spent more than five steps.
- The learning rate is 0.1
- The gamma (discount rate) is 0.99

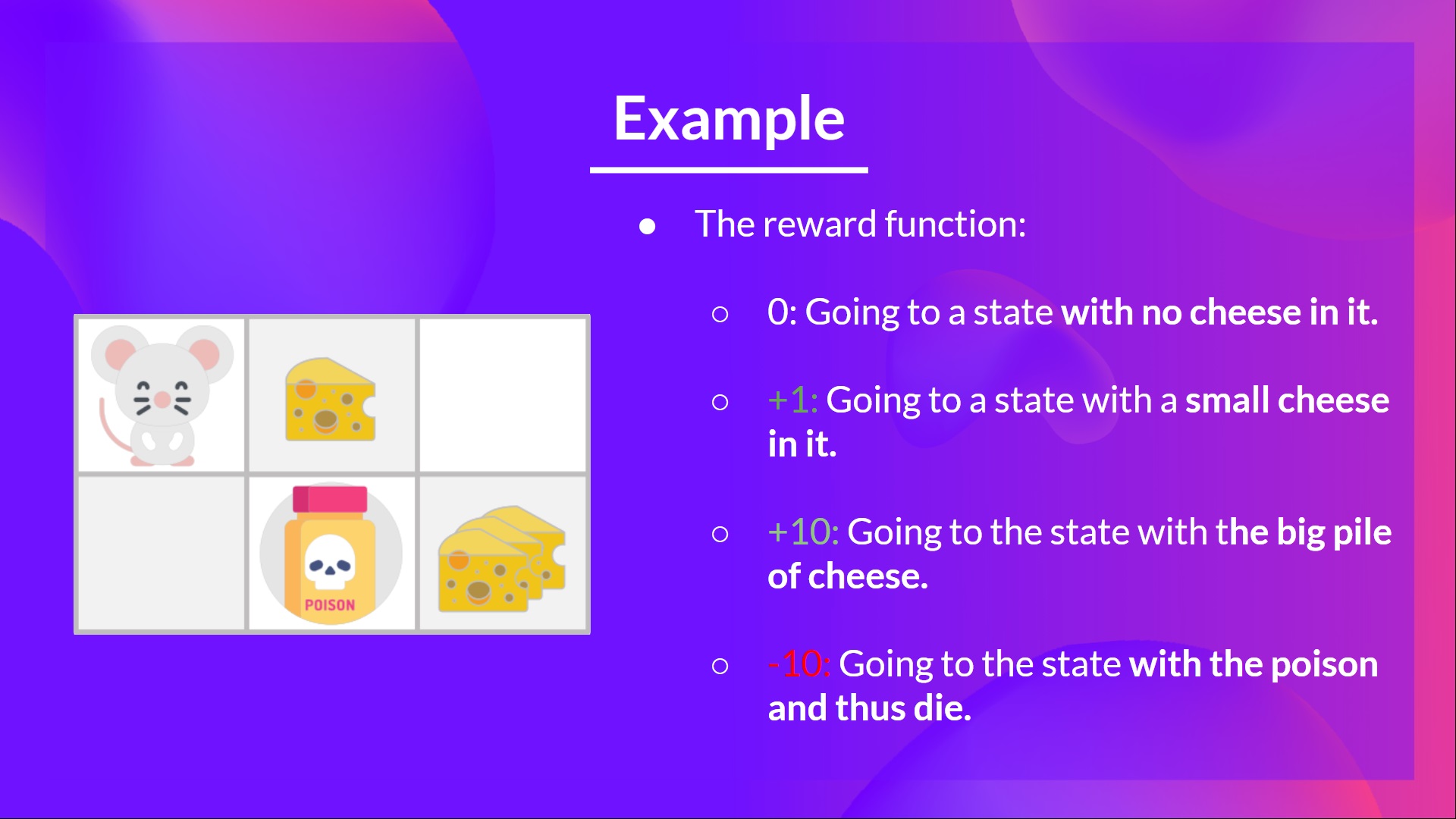
The reward function goes like this:
你是这个迷宫里的一只老鼠。你总是要从同一个起点开始,目标是吃下右下角的一大堆奶酪,避免中毒。毕竟,谁不喜欢奶酪呢?如果我们吃了毒药,吃了一大堆奶酪,或者我们花了五个步骤以上,那么这一集就结束了。学习率是0.1伽玛(贴现率)是0.99迷宫-示例奖励函数是这样的:
- +0: Going to a state with no cheese in it.
- +1: Going to a state with a small cheese in it.
- +10: Going to the state with the big pile of cheese.
- -10: Going to the state with the poison and thus die.
- +0 If we spend more than five steps.
To train our agent to have an optimal policy (so a policy that goes right, right, down), we will use the Q-Learning algorithm.
+0:去没有奶酪的州。+1:去一个有小奶酪的州。+10:带着一大堆奶酪去州。-10:带着毒药去州,这样就死了。+0如果我们花了五个以上的步骤。迷宫-训练我们的代理人有一个最优策略的例子(所以策略是正确的,正确的,向下的),我们将使用Q-学习算法。
Step 1: We initialize the Q-table
步骤1:初始化Q表

So, for now, our Q-table is useless; we need to train our Q-function using the Q-Learning algorithm.
迷宫-例如,就目前而言,我们的Q表是无用的;我们需要使用Q-学习算法来训练我们的Q函数。
Let’s do it for 2 training timesteps:
让我们来做两个训练时间步长:
Training timestep 1:
培训时间第一步:
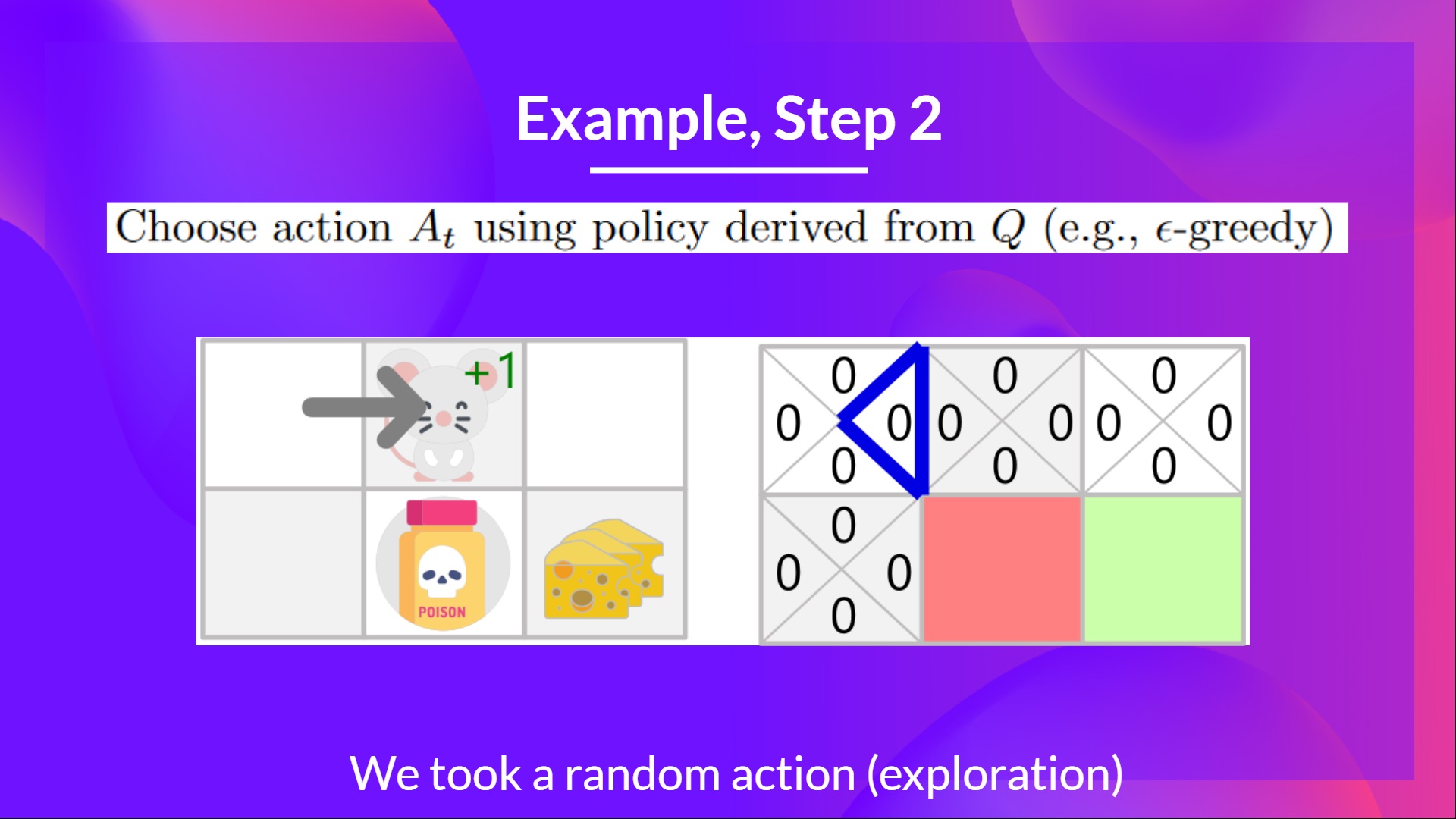
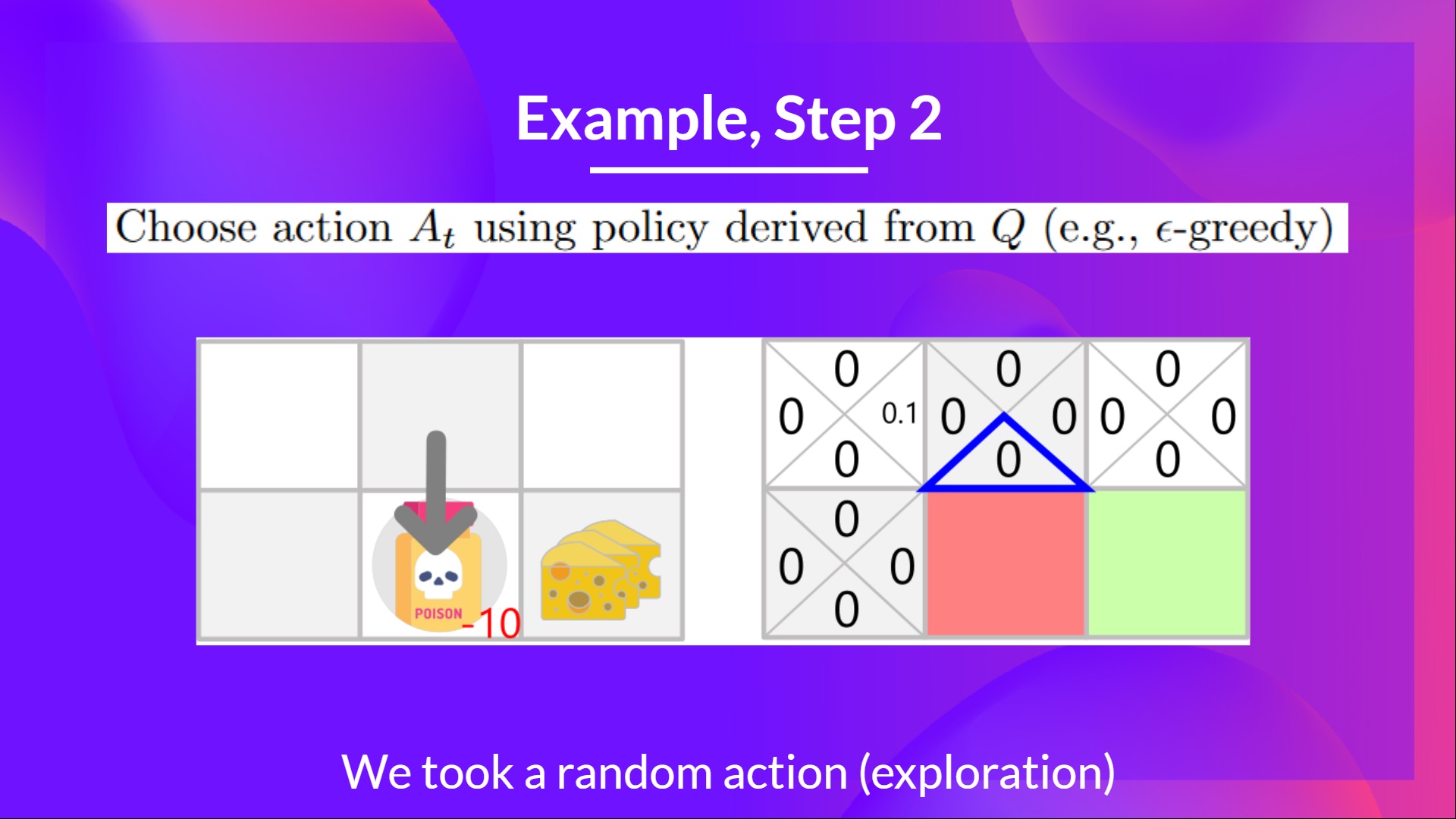
Step 2: Choose action using Epsilon Greedy Strategy
第2步:使用Epsilon贪婪策略选择行动
Because epsilon is big = 1.0, I take a random action, in this case, I go right.
因为epsilon大=1.0,所以我采取随机操作,在本例中,我向右转。
迷宫–例子
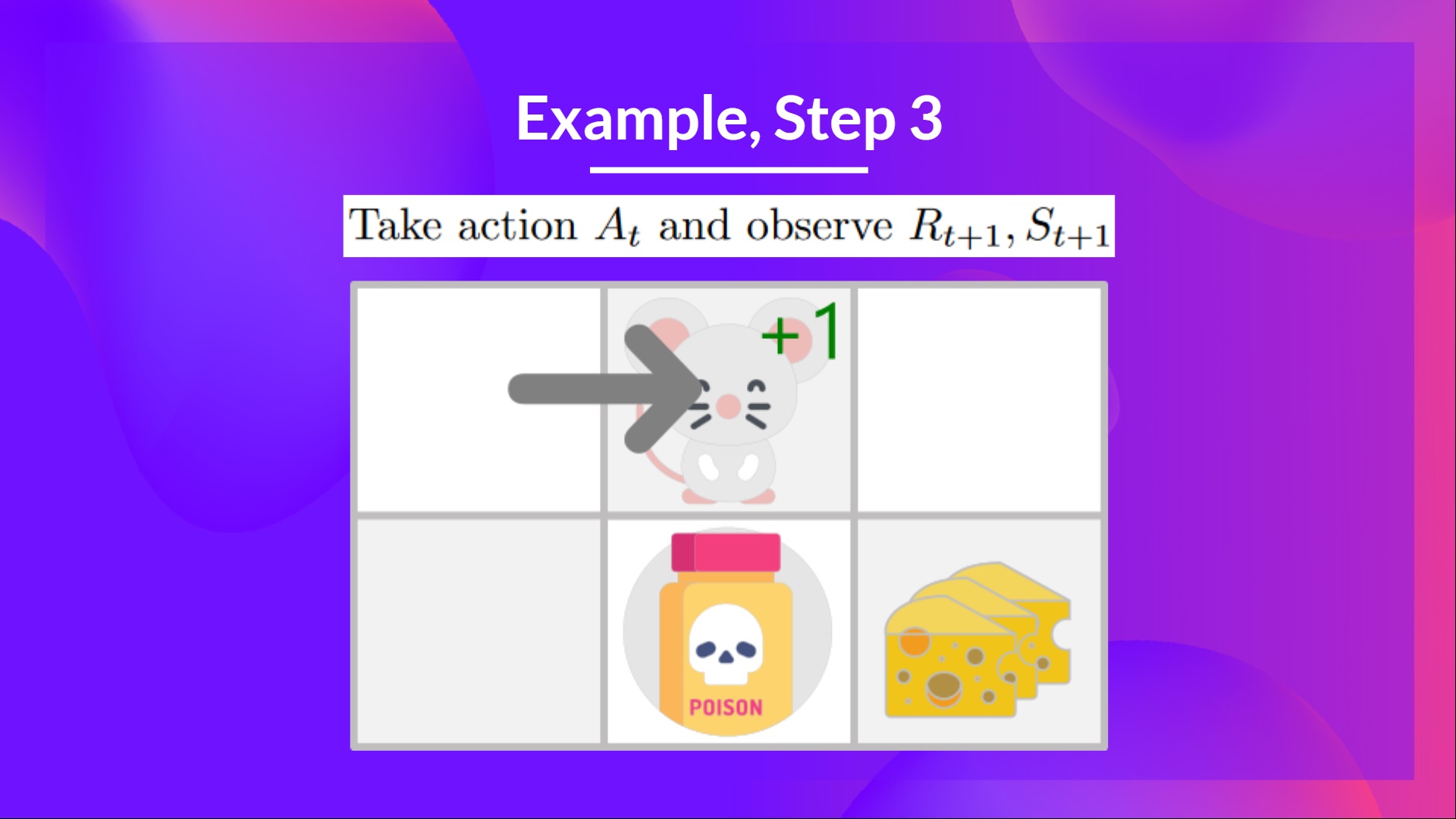
Step 3: Perform action At, gets Rt+1 and St+1
步骤3:在执行操作时,获得RT+1和ST+1
By going right, I’ve got a small cheese, so Rt+1=1R_{t+1} = 1Rt+1=1, and I’m in a new state.
通过向右,我得到了一个小奶酪,所以RT+1=1R_{t+1}=1Rt+1=1,我处于一个新的状态。
迷宫–例子
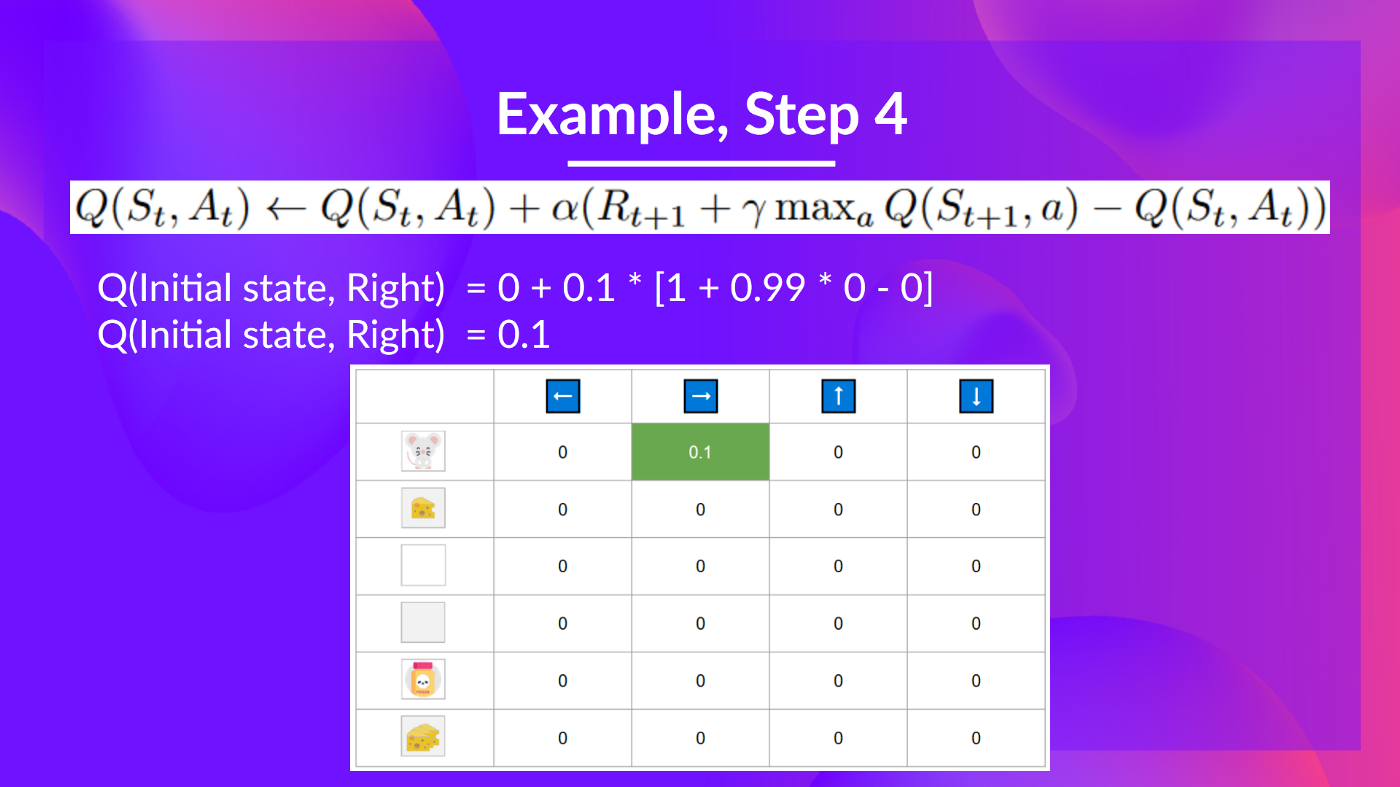
Step 4: Update Q(St, At)
步骤4:更新Q(ST,AT)
We can now update Q(St,At)Q(S_t, A_t)Q(St,At) using our formula.
现在我们可以使用我们的公式更新Q(ST,At)Q(S_t,A_t)Q(ST,At)。

Training timestep 2:
迷宫-示例迷宫-示例培训时间步骤2:
Step 2: Choose action using Epsilon Greedy Strategy
第2步:使用Epsilon贪婪策略选择行动
I take a random action again, since epsilon is big 0.99 (since we decay it a little bit because as the training progress, we want less and less exploration).
我再次采取随机行动,因为epsilon很大,0.99%(因为随着训练的进行,我们想要的探索越来越少,所以我们稍微衰减了一点)。
I took action down. Not a good action since it leads me to the poison.
我采取了行动。这不是一个好的行动,因为它把我引向了毒药。
迷宫–例子
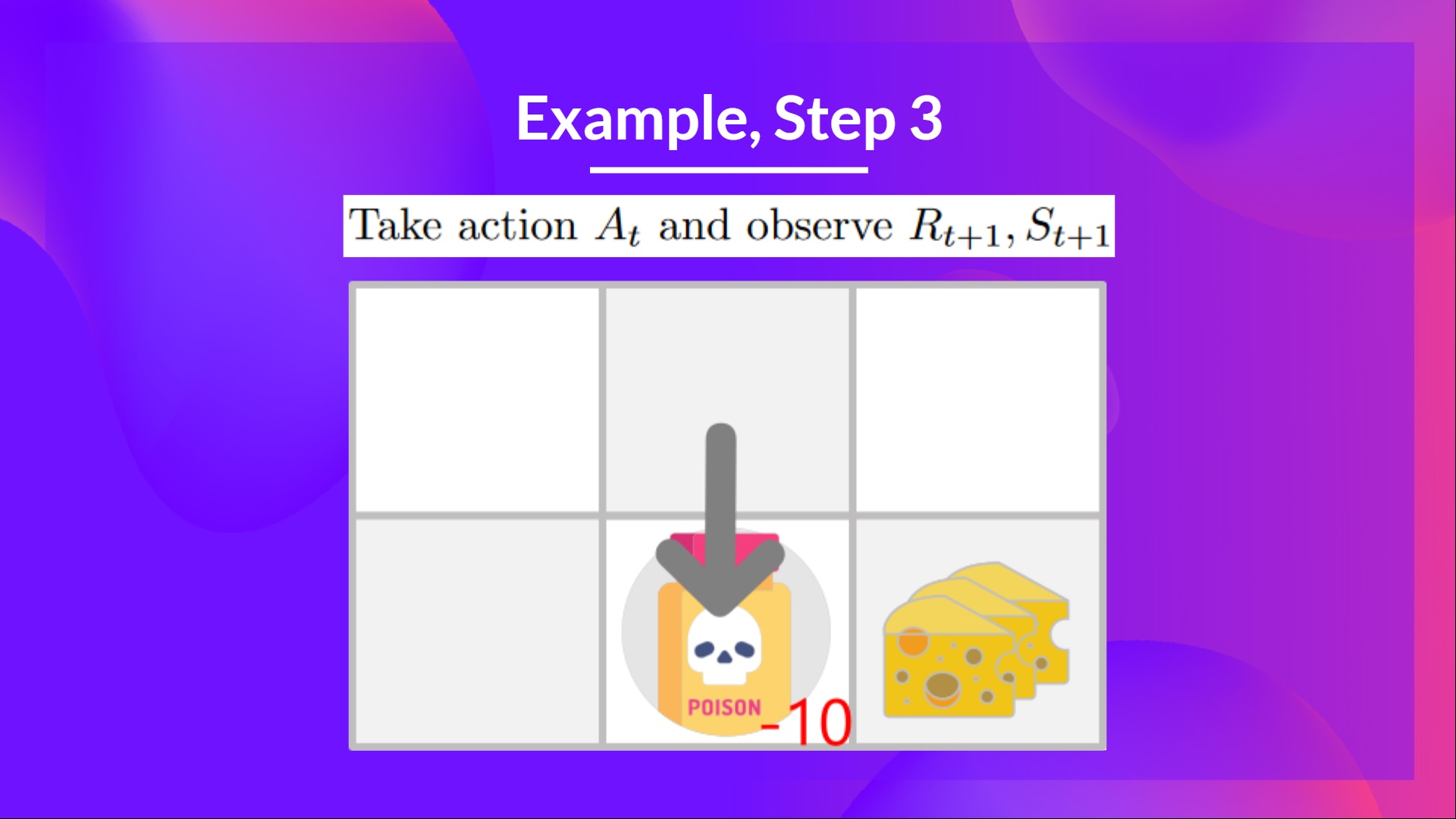
Step 3: Perform action At, gets Rt+1 and St+1
步骤3:在执行操作时,获得RT+1和ST+1
Because I go to the poison state, I get Rt+1=−10R_{t+1} = -10Rt+1=−10, and I die.
因为我进入中毒状态,所以我得到RT+1=−10R_{t+1}=-10Rt+1=−10,然后我就死了。
迷宫–例子
Step 4: Update Q(St, At)
步骤4:更新Q(ST,AT)
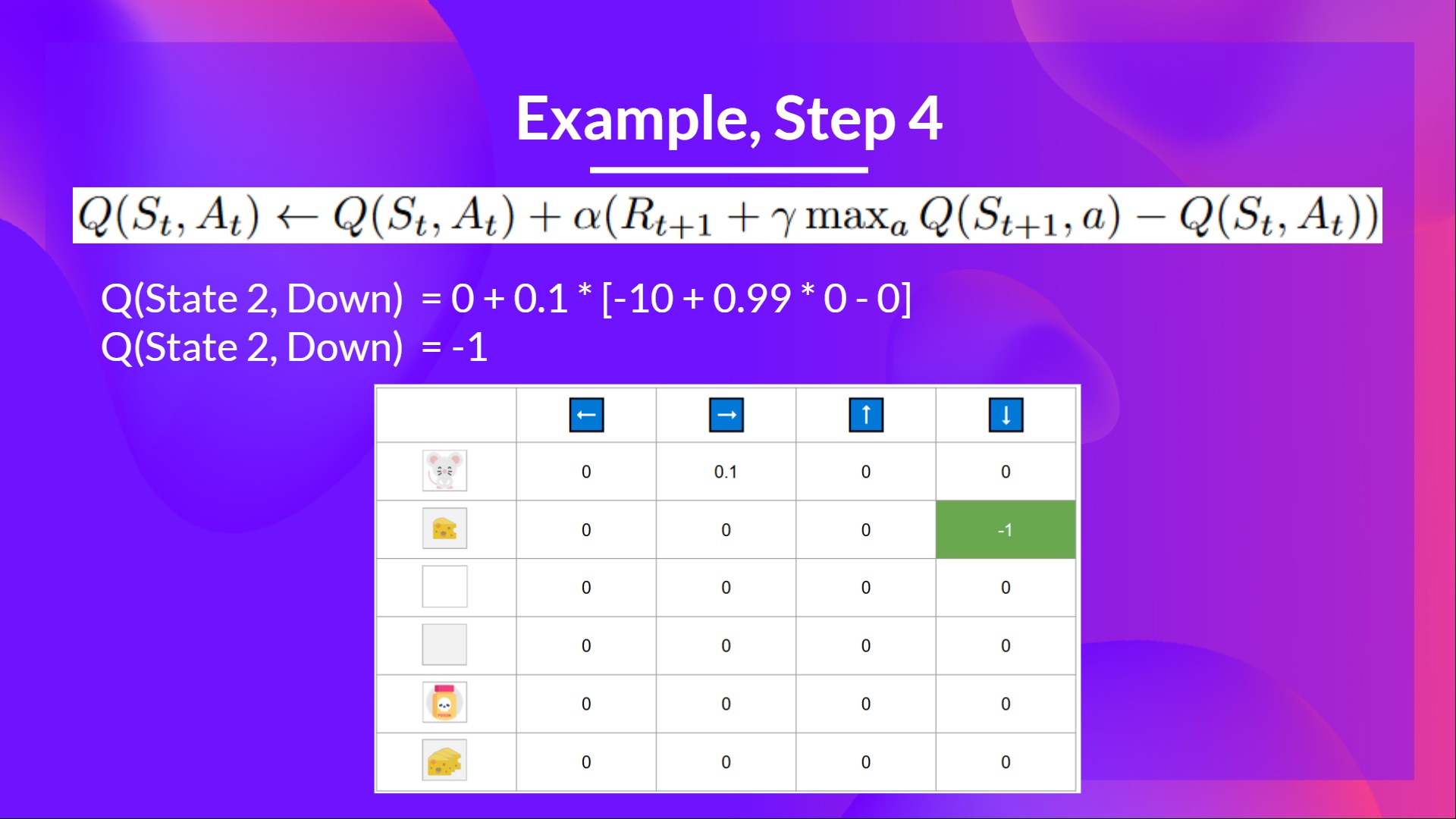
Because we’re dead, we start a new episode. But what we see here is that with two explorations steps, my agent became smarter.
迷宫–因为我们死了,我们就开始新的一集。但我们在这里看到的是,经过两个探索步骤,我的经纪人变得更聪明了。
As we continue exploring and exploiting the environment and updating Q-values using TD target, Q-table will give us better and better approximations. And thus, at the end of the training, we’ll get an estimate of the optimal Q-function.
随着我们继续探索和利用环境,并使用TD目标更新Q值,Q表将给我们越来越好的近似。因此,在训练结束时,我们将得到最优Q函数的估计。