E4-Unit_2-Introduction_to_Q_Learning-D3-The_Bellman_Equation_simplify_our_value_estimation
中英文对照学习,效果更佳!
原课程链接:https://huggingface.co/deep-rl-course/unit5/how-mlagents-works?fw=pt
The Bellman Equation: simplify our value estimation
贝尔曼方程:简化我们的价值估算
The Bellman equation simplifies our state value or state-action value calculation.
贝尔曼方程简化了我们的状态值或状态-作用值的计算。

With what we have learned so far, we know that if we calculate the V(St)V(S_t)V(St) (value of a state), we need to calculate the return starting at that state and then follow the policy forever after. (The policy we defined in the following example is a Greedy Policy; for simplification, we don’t discount the reward).
贝尔曼方程与我们到目前为止所了解的,我们知道,如果我们计算V(ST)V(S_T)V(ST)(一个州的值),我们需要计算从该州开始的回报,然后永远遵循该政策。(我们在下面的例子中定义的政策是贪婪的政策;为了简化,我们不打折奖励)。
So to calculate V(St)V(S_t)V(St), we need to calculate the sum of the expected rewards. Hence:
因此,要计算V(ST)V(S_T)V(ST),我们需要计算预期回报的总和。因此:
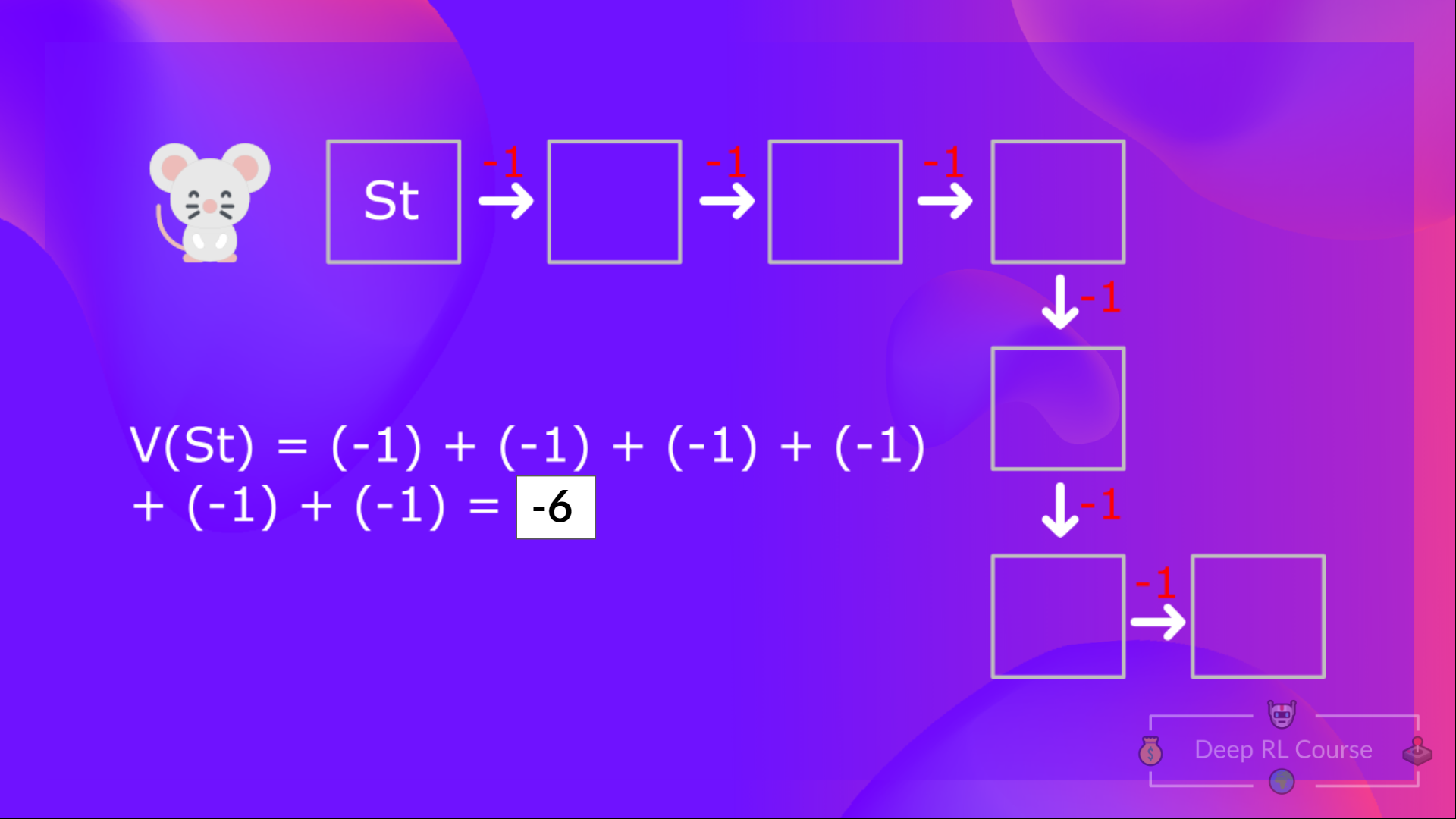
To calculate the value of State 1: the sum of rewards if the agent started in that state and then followed the greedy policy (taking actions that leads to the best states values) for all the time steps.
Then, to calculate the V(St+1)V(S_{t+1})V(St+1), we need to calculate the return starting at that state St+1S_{t+1}St+1.
计算状态1的值的贝尔曼方程:如果代理从该状态开始,然后在所有时间步骤中遵循贪婪的政策(采取导致最佳状态值的行动),则奖励的总和。然后,为了计算V(ST+1)V(S_{t+1})V(ST+1),我们需要计算从该状态ST+1S_{t+1}ST+1开始的回报。
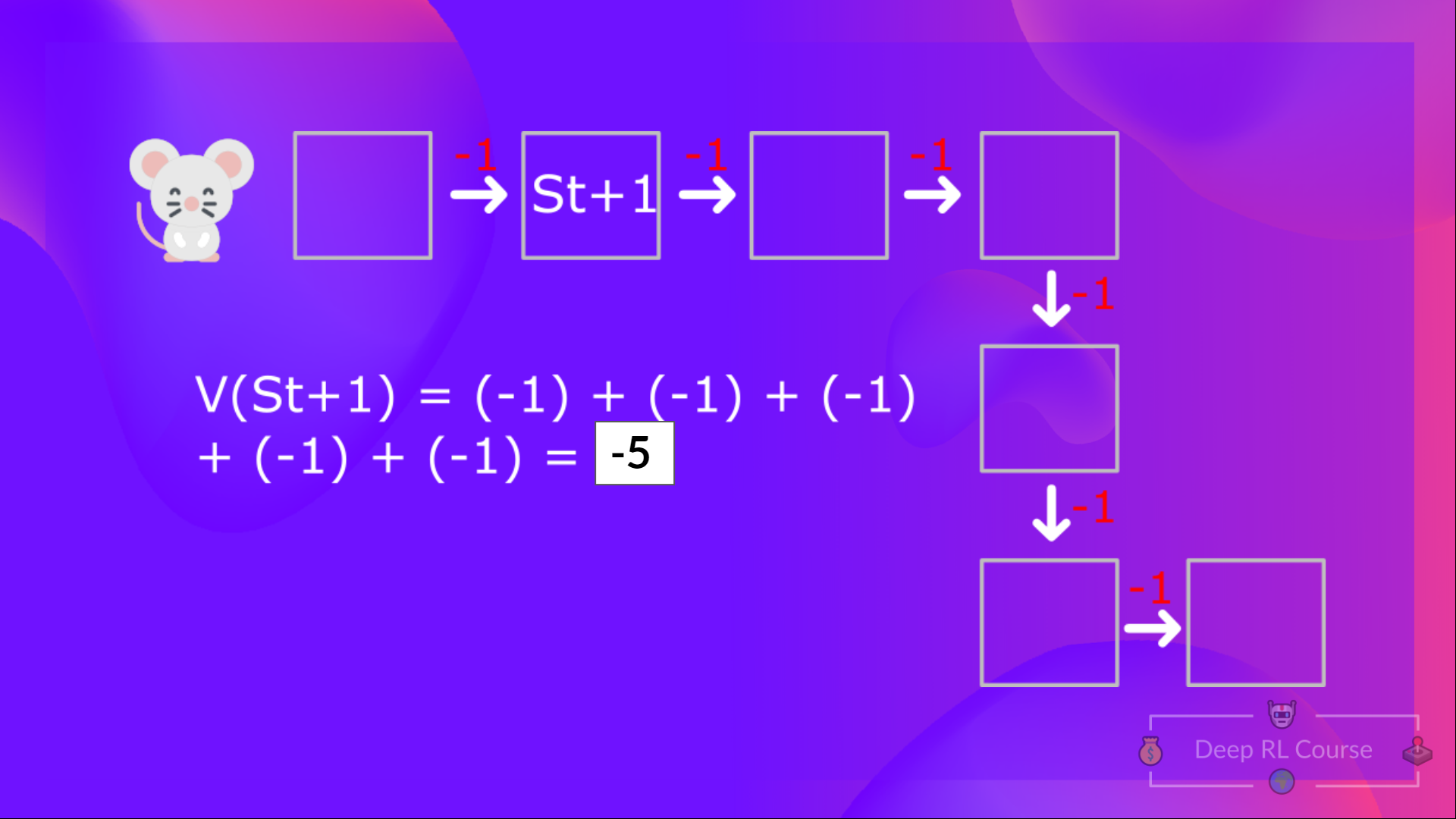
To calculate the value of State 2: the sum of rewards if the agent started in that state, and then followed the policy for all the time steps.
So you may have noticed, we’re repeating the computation of the value of different states, which can be tedious if you need to do it for each state value or state-action value.
计算状态2的值的贝尔曼方程:如果代理在该状态下开始,则奖励的总和,然后在所有时间步骤中遵循第一项政策。所以你可能已经注意到了,我们在重复计算不同状态的值,如果你需要对每个状态值或状态操作值进行计算,这可能会很繁琐。
Instead of calculating the expected return for each state or each state-action pair, we can use the Bellman equation. (hint: if you know what Dynamic Programming is, this is very similar! if you don’t know what it is, no worries!)
我们可以使用贝尔曼方程,而不是计算每个状态或每个状态-行动对的预期回报。(提示:如果您知道什么是动态编程,这一点非常相似!如果您不知道这是什么,也不用担心!)
The Bellman equation is a recursive equation that works like this: instead of starting for each state from the beginning and calculating the return, we can consider the value of any state as:
Bellman方程式是一个递归方程式,其工作原理如下:我们可以将任何状态的值视为:
The immediate reward Rt+1R_{t+1}Rt+1 + the discounted value of the state that follows ( gamma∗V(St+1)gamma * V(S_{t+1}) gamma∗V(St+1) ) .
即时回报RT+1R_{t+1}RT+1+(伽马∗V(ST+1)伽马*V(S_(t+1))伽马∗V(ST+1))之后的状态的折扣值。
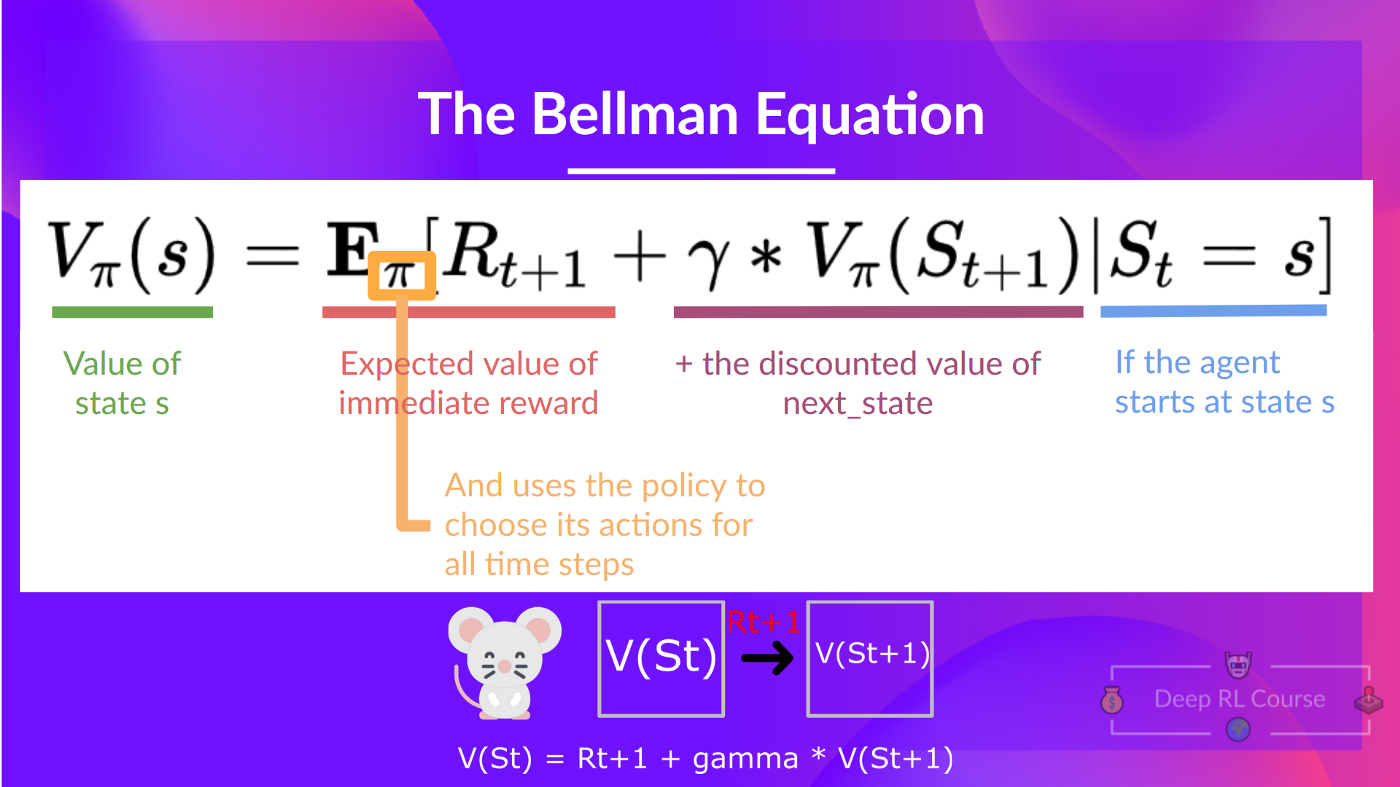
If we go back to our example, we can say that the value of State 1 is equal to the expected cumulative return if we start at that state.
贝尔曼方程如果我们回到我们的例子,我们可以说,状态1的值等于预期累积收益,如果我们从那个状态开始的话。

To calculate the value of State 1: the sum of rewards if the agent started in that state 1 and then followed the policy for all the time steps.
计算状态1的值的贝尔曼方程:如果代理从该状态1开始,然后在所有时间步骤中都遵循最高政策,则奖励的总和。
This is equivalent to V(St)V(S_{t})V(St) = Immediate reward Rt+1R_{t+1}Rt+1 + Discounted value of the next state γ∗V(St+1)\gamma * V(S_{t+1})γ∗V(St+1)
这相当于V(ST)V(S_{t})V(ST)=即时报酬RT+1R_{t+1}RT+1+下一状态的折扣值∗V(ST+1)\γV(S_{t+1})GammaV(ST+1)γV(ST+1γ)
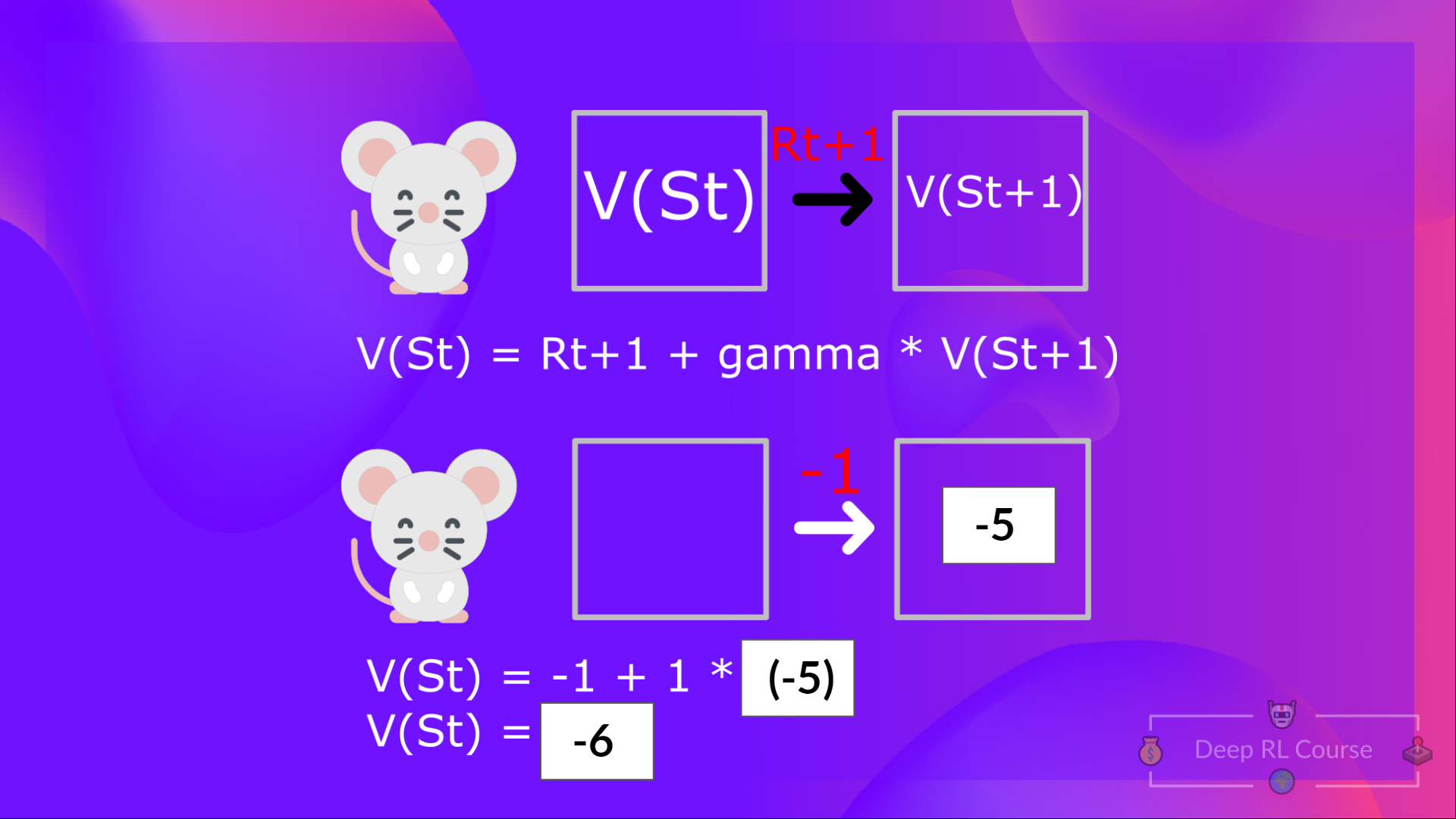
For simplification, here we don’t discount so gamma = 1.
In the interest of simplicity, here we don’t discount, so gamma = 1.
But you’ll study an example with gamma = 0.99 in the Q-Learning section of this unit.
为了简化贝尔曼方程,这里我们不考虑,所以伽马=1。为了简单起见,我们不考虑,所以,伽马=1。但你将在本单元的Q-学习部分研究一个伽马=0.99的例子。
- The value of V(St+1)V(S_{t+1}) V(St+1) = Immediate reward Rt+2R_{t+2}Rt+2 + Discounted value of the next state ( gamma∗V(St+2)gamma * V(S_{t+2})gamma∗V(St+2) ).
- And so on.
To recap, the idea of the Bellman equation is that instead of calculating each value as the sum of the expected return, which is a long process, we calculate the value as the sum of immediate reward + the discounted value of the state that follows.
V(ST+1)V(S_{t+1})V(ST+1)=即时回报RT+2R_(t+2)RT+2+下一状态的折扣值(伽马∗V(ST+2)伽马*V(S_{t+2})伽马∗V(ST+2))。简而言之,贝尔曼方程的思想是,不是将每个值计算为预期回报的和,这是一个漫长的过程,我们计算该值为即时回报+随后状态的折扣值的和。
Before going to the next section, think about the role of gamma in the Bellman equation. What happens if the value of gamma is very low (e.g. 0.1 or even 0)? What happens if the value is 1? What happens if the value is very high, such as a million?
在进入下一节之前,先考虑一下伽马在贝尔曼方程中的作用。如果Gamma的值非常低(例如0.1甚至0),会发生什么情况?如果值为1,会发生什么情况?如果价值非常高,例如一百万,会发生什么?